Big Chico Creek Water Quality Monitoring
Main | Data Table | Temperature | Electrical Conductivity | pH | Dissolved Oxygen | Turbidity | Nutrients | Metals
Disclaimer: Data presented on this webpage were acquired following internal (non-standard) procedures and are therefore for information purposes only and not citable until independent peer review and publication.
Dissolved Oxygen
What is dissolved oxygen?
Resources: Water Science School - Dissolved Oxygen and Water (USGS), Environmental Learning Center - Dissolved Oxygen (Fondriest Environmental)
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is the amount of oxygen dissolved in the water and is essential for aquatic organisms to survive in the stream. Dissolved oxygen is inversely related to water temperature, for example, higher temperatures create low dissolved oxygen conditions. Dissolved oxygen is also affected by atmospheric pressure, elevation, and in-stream biological process. Photosynthesis contributes dissolved oxygen, while microbial respiration consumes dissolved oxygen. Running, cold water are ideal conditions for dissolved oxygen, whereas, stagnant water is warmer and typically contains a high concentration of organic material that can lead to eutrophic conditions, meaning there is a lack of oxygen in the water, through microbial decomposition.
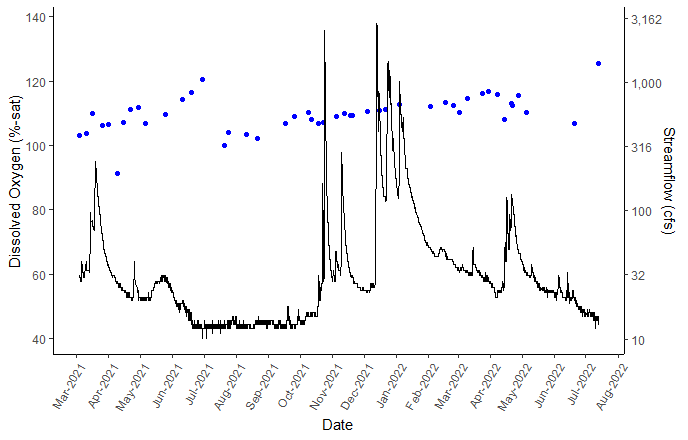
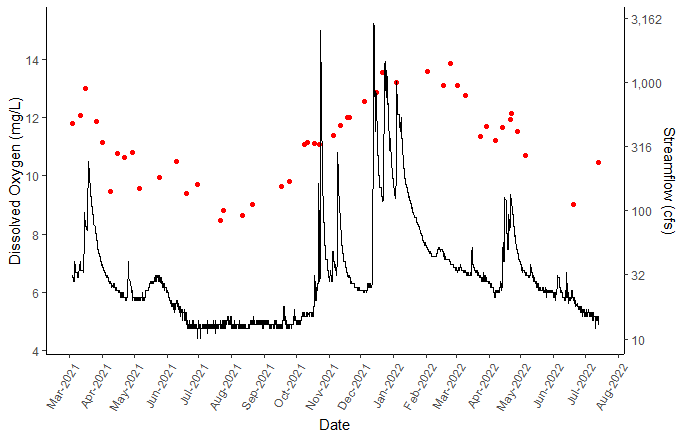
DO was measured at percent saturation where 100% means the water is “saturated”, holding as much dissolved oxygen as is possible for its temperature and pressure. Even at 100% saturation, the concentration of dissolved oxygen (mg/L) varies with pressure, temperature, and salinity.
Dissolved Oxygen and Streamflow in Big Chico Creek
![]()
Dissolved Oxygen Saturation and Streamflow in Big Chico Creek
![]()