Alcohol Basics
eCHECKUP TO GO
What is Alcohol?
Ethyl alcohol, or ethanol, is an intoxicating ingredient found in beer, wine, and liquor. It is a central nervous system depressant that is rapidly absorbed from the stomach and small intestine into the bloodstream.
Alcohol is metabolized in the liver by enzymes. However, the liver can only metabolize a small amount of alcohol at a time, leaving the excess alcohol to circulate throughout the body. The intensity of the effect of alcohol on the body is directly related to the amount consumed.
Alcohol consumption is associated with a variety of short and long term health risks, including motor vehicle crashes, violence, sexual risk behaviors, high blood pressure, and various cancers. The risk for these harms increases with the amount of alcohol you drink. For some conditions, like some cancers, the risk increases even at very low levels of alcohol consumption.1(opens in new window)
Alcohol & Your Health
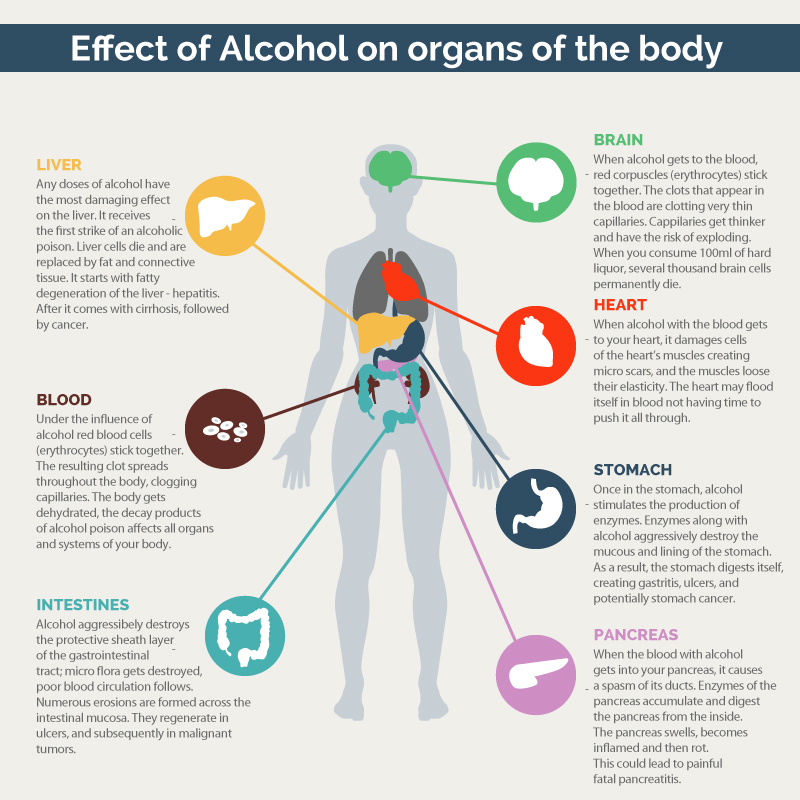
For more information about how alcohol use can affect your health, check out the CDC's website(opens in new window).
Standard Drink Size
ONE serving or DOSE of alcohol equals…
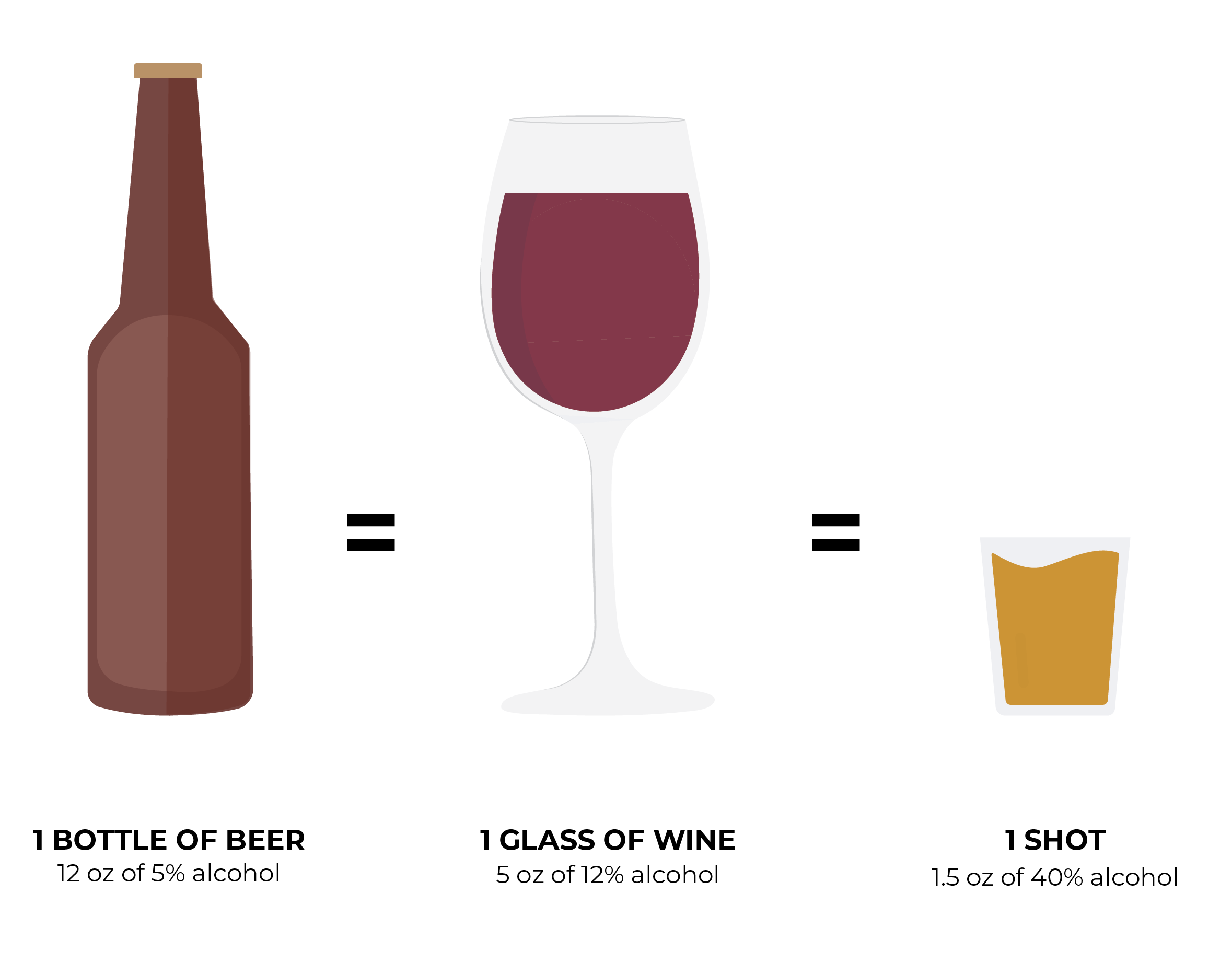
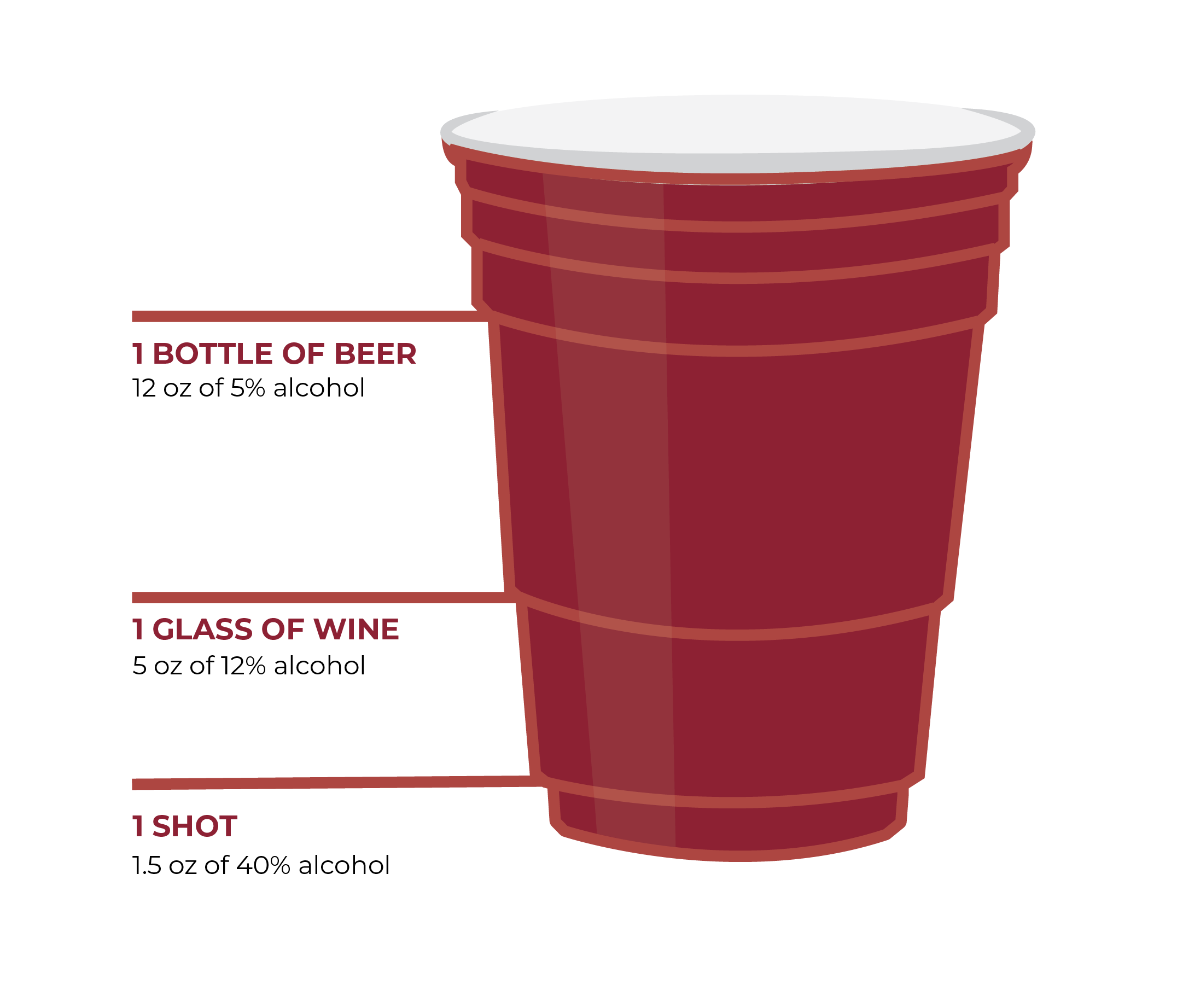
This is a general rule, based on the average ABV (alcohol by volume) of each type of drink. ABV refers to the percent of pure alcohol in a drink, meaning that drinks with a higher ABV will be stronger and less is needed to equal one dose, or standard drink.
Different kinds of beer, wine, or hard alcohol will have different ABVs, so it's always important to check the ABV of what you're drinking.
Excessive vs. Moderate Drinking
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, excessive drinking includes binge drinking, heavy drinking, and any drinking by pregnant people or people younger than the age of 21.
Moderate Drinking
For those over 21 who choose to drink, moderating drinking is the best way to lower the risks associated with consuming alcohol. Moderate drinking for women is no more than 1 drink per day, while moderate drinking for men is no more than 2 drinks on any given day.
Binge Drinking
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism defines binge drinking as a pattern of high-risk drinking that brings a person’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) to 0.08 or above.
This typically happens when men consume 5 or more drinks or women consume 4 or more drinks in about 2 hours.
Heavy Drinking
For women, heavy drinking is defined as consuming 8 or more drinks per week, while for men heavy drinking is defined as consuming 15 or more drinks per week.
Blood Alcohol Content
Blood Alcohol Content, or BAC, is the concentration of alcohol in one's bloodstream, expressed as a percentage. BAC is used to determine whether a person is legally intoxicated, especially in operating or attempting to operate a motor vehicle. In California, .08 or above is considered legal intoxication.
Do NOT rely on a BAC calculator to accurately estimate your BAC levels and make an assessment if it is safe for you to drive. In fact, it can still be unsafe to drive even if you are under the legal limit. There are many factors that can influence your BAC, including: number of drinks consumed, period of time drinks consumed, gender, weight, and personal health.
.020 - Light to moderate drinkers begin to feel some effects
.040 - Most people begin to feel relaxed
.060 - Judgment is somewhat impaired
.080 - Definite impairment of muscle coordination and driving skills.
.100 - Clear deterioration of reaction time and control. This is legally drunk in all states.
.120 - Vomiting usually occurs
.150 - Balance and movement are impaired. Here the equivalent of a 1/2 pint of whiskey is circulating in the blood stream.
.200 - Most people begin to experience blackouts
.300 - Many people lose consciousness
.400 - Most people lose consciousness and some die
.450 - Breathing stops. This is a fatal dose for most people.
The chart above is an example of how BAC can vary by weight and number of drinks over time. This chart should not be used to gauge your own level of intoxication. Click here(opens in new window) for a BAC calculator that can be used to further learn the effects of BAC.
